Since the 1980s igm has been a leader in the design, manufacture and installation of sensor controlled welding and cutting robot systems. Besides efficient overall systems, igm Australia can develop solutions as individual as your business, improving efficiency, quality and output.


01.
Extensive range
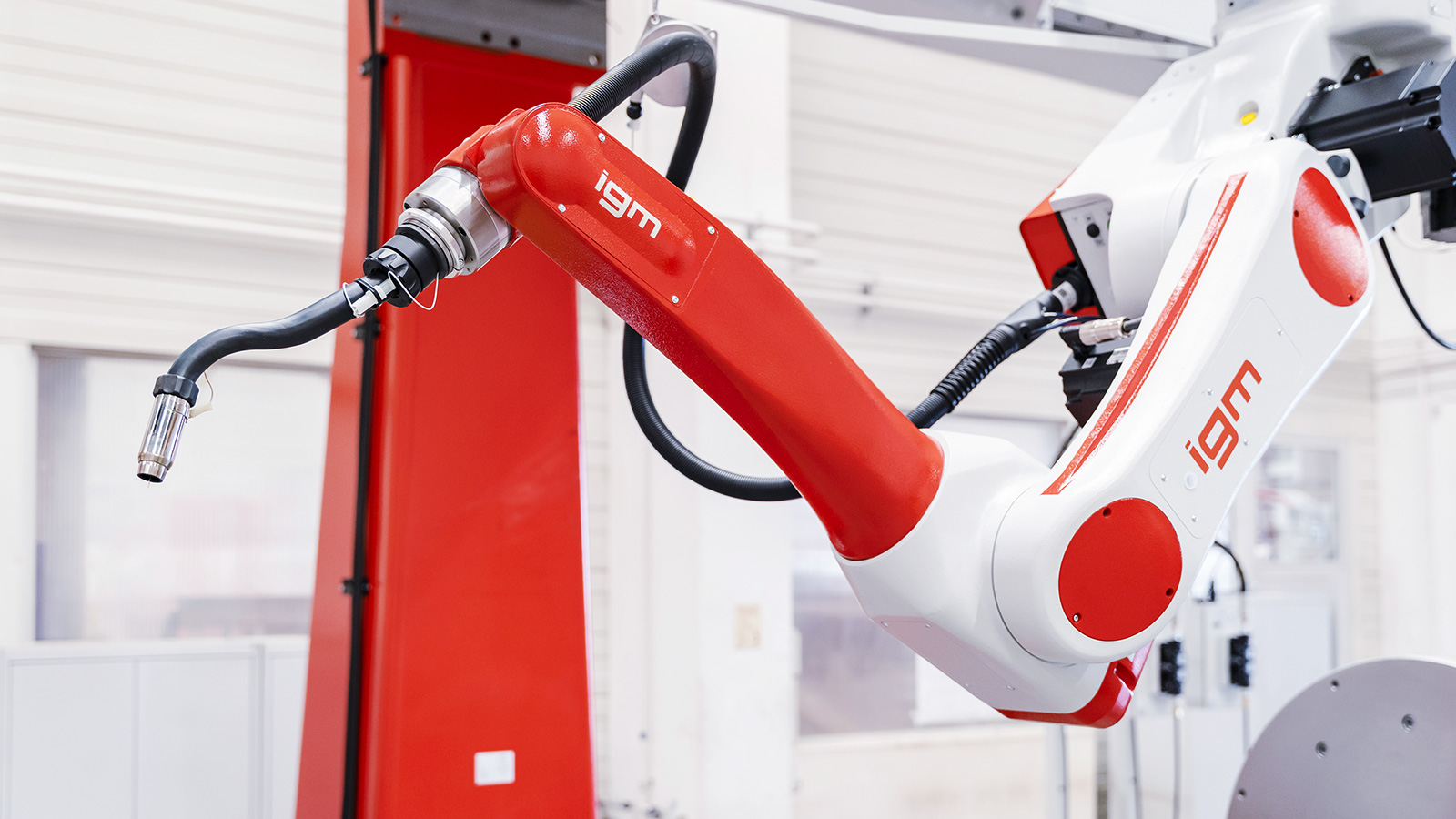
Over four decades of experience in the development of welding robots and planning of production plants, appear in an extensive range of system modules. The main module is the igm Robot Series RTE 400.
Benefits, typical for igm robots:
01. cont.
The particular features of the RTE 400 modular robot system are the extremely slim robotic arms, optimized for weight and rigidity. For axes 2 and 4 there are different lengths available. The right range of movement can be selected for any application.
The highly dynamic, maintenance-free AC servo motors and outstanding characteristics of the joint construction of rigid cast aluminium, guarantee a high rotational speed and quick acceleration on all axes. The motors are equipped with holding brakes – there is no need for calibration after turning the robot off. The drive forces are transmitted by maintenance-free Cyclo gearboxes. Their use permits not only rapid positioning and high-precision path accuracy, but also keeps the number of parts used – and thus the number of replacement parts needed – low.
Arc welding in high precision
The robots are designed specifically for arc welding. One unique feature is that all the media needed for welding are directed first through the main axis and then through the hollow shaft into the wrist axis, allowing the welding torch to complete two full turns. The result is a significant advantage in terms of accessibility to tight work pieces and in circular seams.
Perfection of arc means that the robots are working with 6, 7 or 8 rotary axes in a solid aluminium cast construction, mounted either upright or in suspended position.
Axis arrangement
Not only the drive media of the robot run through axis 1 in the RTE robot system, but also the welding media such as the cooling hoses, gas hoses, cable conduit hoses and water cooled cable for the welding current connection, as well as the control cable for the wire feed.
To keep the robot and the welding equipment slim at the base, the wire feed is integrated into axis 1 and protected from environmental influences with a cover.
An additional axis is provided for any application that requires a special range of motion – the rotating base. This is entirely integrated into the kinematic chain of the robot control system and, together with axis 1, permits an enormously expanded sphere of motion. The maximum work zone radius of 5200mm can be extended as needed with the external rotation and linear axes.
RTE 400 – Robot types:
Multipurpose igm robot
Welding, cutting, bevelling and more – multitasking by igm.
igm robots can do everything. Besides welding they are also able to cut, bevel, move, pre-heat and more. In this case only the tools need to be exchanged. A real multitasking robot!
Examples for multipurpose application:

02.
Concept of RCE control system
The control system is fully digitally controlled. This means there are only digital signal processors (DSP) involved in the entire control system and no analogue electronic components. All the components of the control system (such as the control cabinet, welding power source, each axis and the teach pendant) are linked by a digital bus system.
A fully digital robot control system brings the following advantages:
02. cont.
By using modular drive technology and standard PC components a high reliability is guaranteed and the ability to remain constantly at the cutting edge of technology.
Due to the used standard PC components, diagnosis and exchange of components are easy possible also by the customer’s engineers.
The complete control system for up to 8 robot axes and all external NC axes is included in a compact control cabinet connected to the robot, the teach pendant, the operating cassette, the external axes, and the power source by cables, pluggable on both sides.
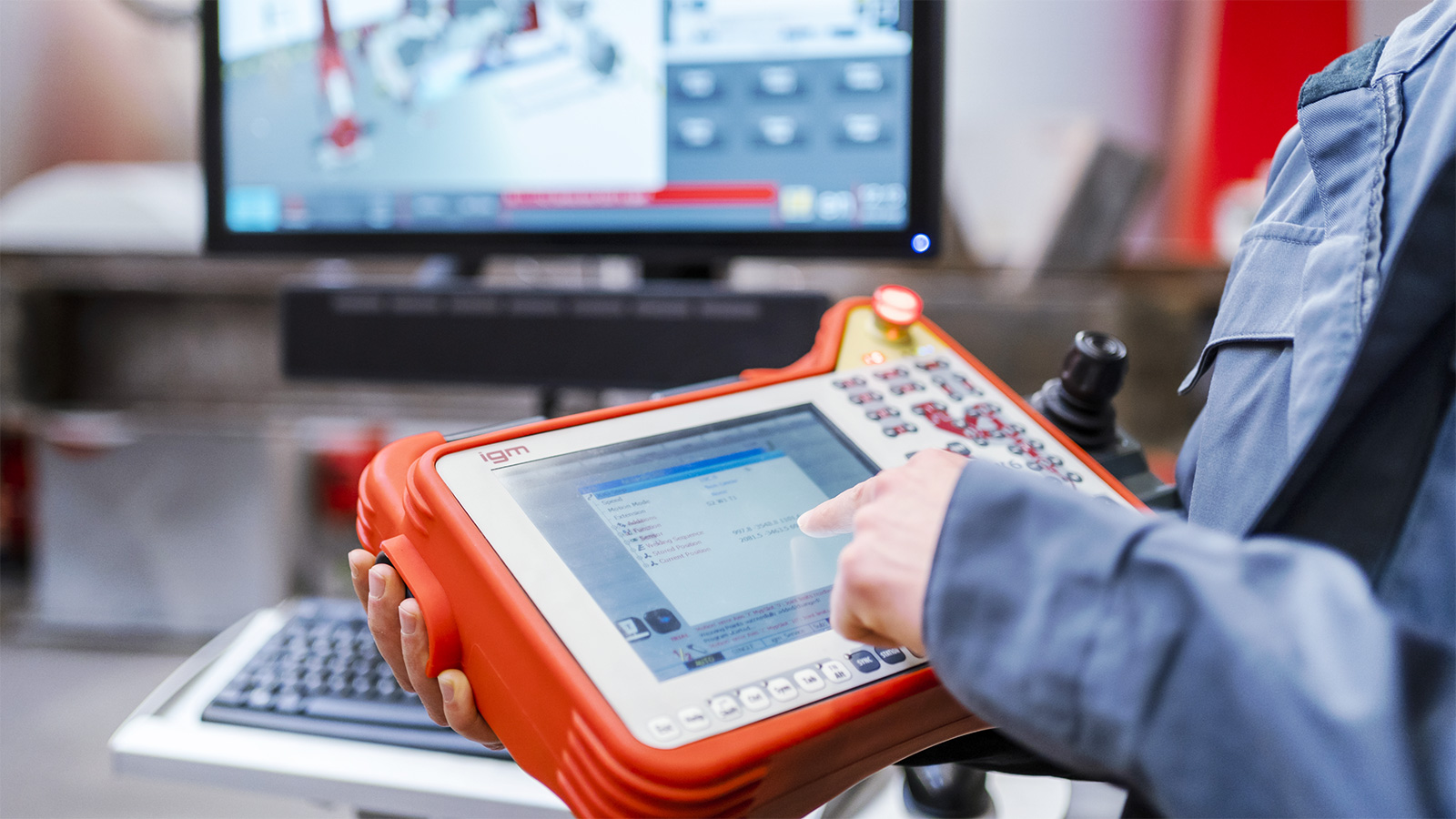
igm Teach Pendant K6
As a key element of the RCE control system, the unique teach pendant K6 assembles all the control functions of the RCE control system. No additional keyboard is necessary.
The industrial design award-winning lightweight teach pendant is made out of a high resistant plastic mould and a keyboard panel at topside with an embedded LCD touch screen. The sensible buttons are palpable to enable the operator to touch and feel each button even with working gloves on, compared to a touch screen display.
The revolutionary and widely favoured shape of the teach pendant allows a right hand and left operation as well as many other holding positions.
A clear and simple display of each axis button allows the operator a distinctive movement of each axis without pushing the wrong axis button my mistake.
A courser block offers easy navigation in the RCE software menus and replaces any necessary mouse.
The control PC uses Windows 10 embedded and Linux embedded. The transfer of process data relevant to security takes place with Safety over EtherCAT (FSoE).
Characteristics of the
K6 Teach Pendant

03.
03. cont.
Robonet
igm software for network operation and remote access from an arbitrary PC to the robot control.
iSDES Embedded
iSDES Embedded is a weld seam and operating data acquisition system for monitoring, documentation and quality assurance of welding processes, as well as for the evaluation of operating data at partially, or fully automated welding robot systems. The iSDES integrated on the control system offers the possibility to record, monitor and evaluate the parameters decisive for the quality as well as the operationally relevant data.
iSDES Embedded functions:
Smartstep
Smartstep is a software product for igm robot controls which generates interactive step programs with templates via program assembling. Time and costs for the development of robot programs are important, especially with small batch sizes. Smartstep offers an easy alternative for the assembly of previously created program parts which are prepared and saved in the library. It allows to built an executable robot program with an interactive input window. Smartstep is mainly used for programming workpieces with few repetitive seams.
iPAT
iPAT (igm Program Assembly Tool) is a very powerful tool which can be used for offline manipulation and the assembling of step programs (template programs). iPAT allows to enter numeric values related to workpiece length and position changes. The goal of iPAT is to chain template programs after each other to a target program. In doing so, certain step ranges are taken from a template program, will be shifted on the robot or the tracks and copied together to a target program through a simple input dialog. iPAT can also be used for shifts within one single step program.
iCP visualisation software
iCP provides a variety of different visualisations and reports of the status of a robot cell. With a PLC interface, it is easy to connect it to the machine. Additionally it allows the integration of various devices such as PC, tablet or smartphone. All robot stations with their status concerning actual runtime and remaining runtime as well as the current program could be shown at a glance.
Furthermore, a live display of each robot cell together with their status reports can be visualised. The workpiece tracking tool shows the development of the workpiece with all processing steps including its emergency strategies. For the conclusive analysis of the manufacturing process, the SQL data base provides various evaluation possibilities. For example, the availability of the machine and its probability of error as well as the productivity per shift / period of time can be calculated. The user interface is set up during the commissioning of the robot cell and is individually adjusted on the users needs while maintaining all standard functions.

04.
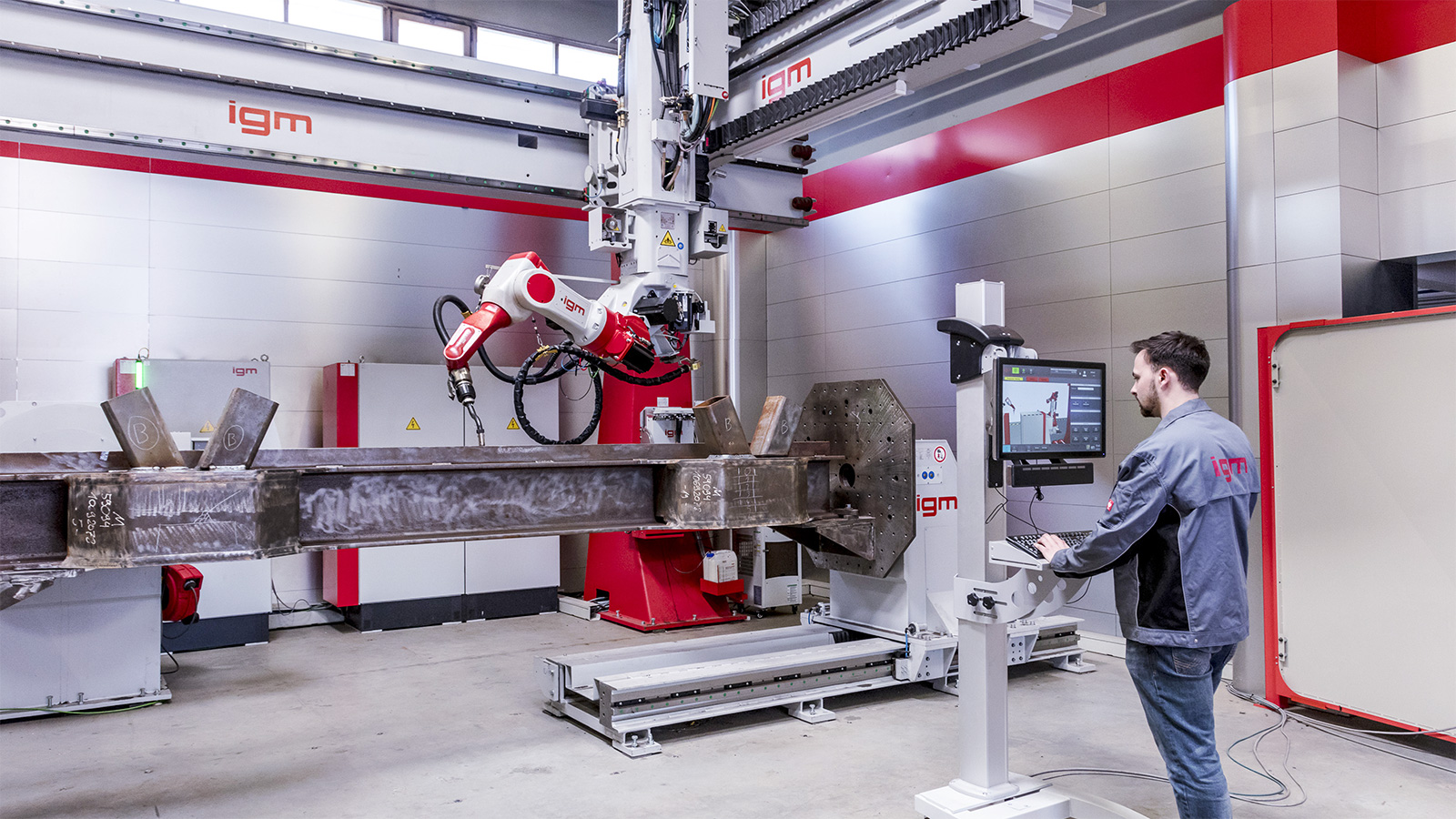
Precise collision control
Operational availability of the robot installation for production is increased by using an off-line system for generating robot programs. While saving time, programs may be prepared more conveniently in an office environment and simulation test runs (accessibility, computation of cycle time) may be performed. Collisions of the robot with the workpiece or fixtures may be detected at an early stage.
Special features:
04. cont.
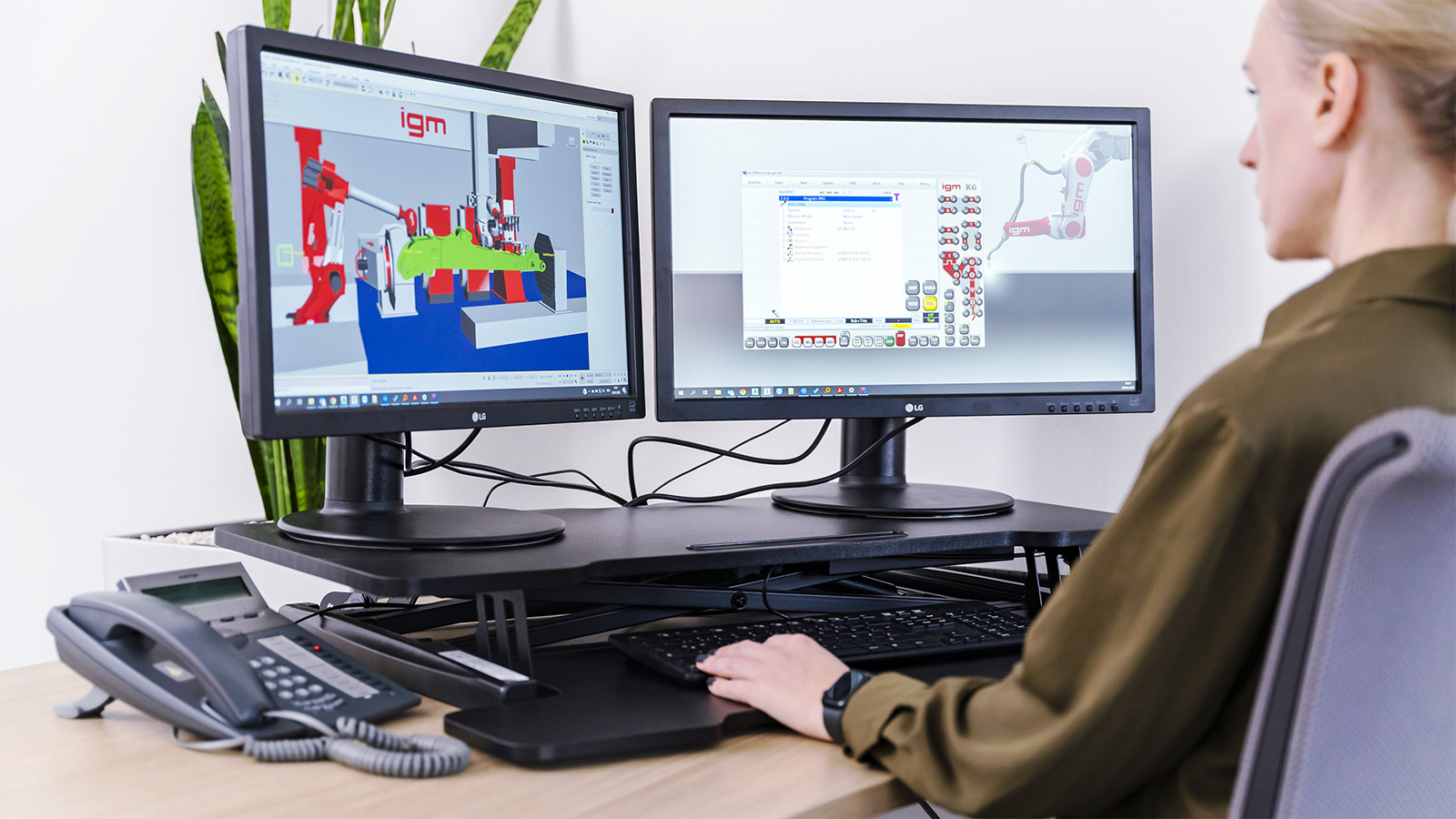
Offline programming – Online working
Simple robot programming is available through the self developed PC-based offline programming system, using the original software of the robot control system and the teach pendant K6.
Offline programming involves work piece oriented programming in 3D mode using a PC and simulation software. The workpiece is first imported into the programming system as 3D-CAD geometry, then the movements of the robot are determined.
For path generation and definition of the processing parameters, a number of automatic functions as well as data bases stored in the control system are available.
It is a simple system identical to that for programming the robot system on the factory floor, but with a significant advantage: When the teach pendant K6 is employed, an identical software is used for all calculations. This means that conversions of machine parameters or robot programmes of any kind are unnecessary. All program changes of the system can be processed using the offline system without any conversion losses.

05.
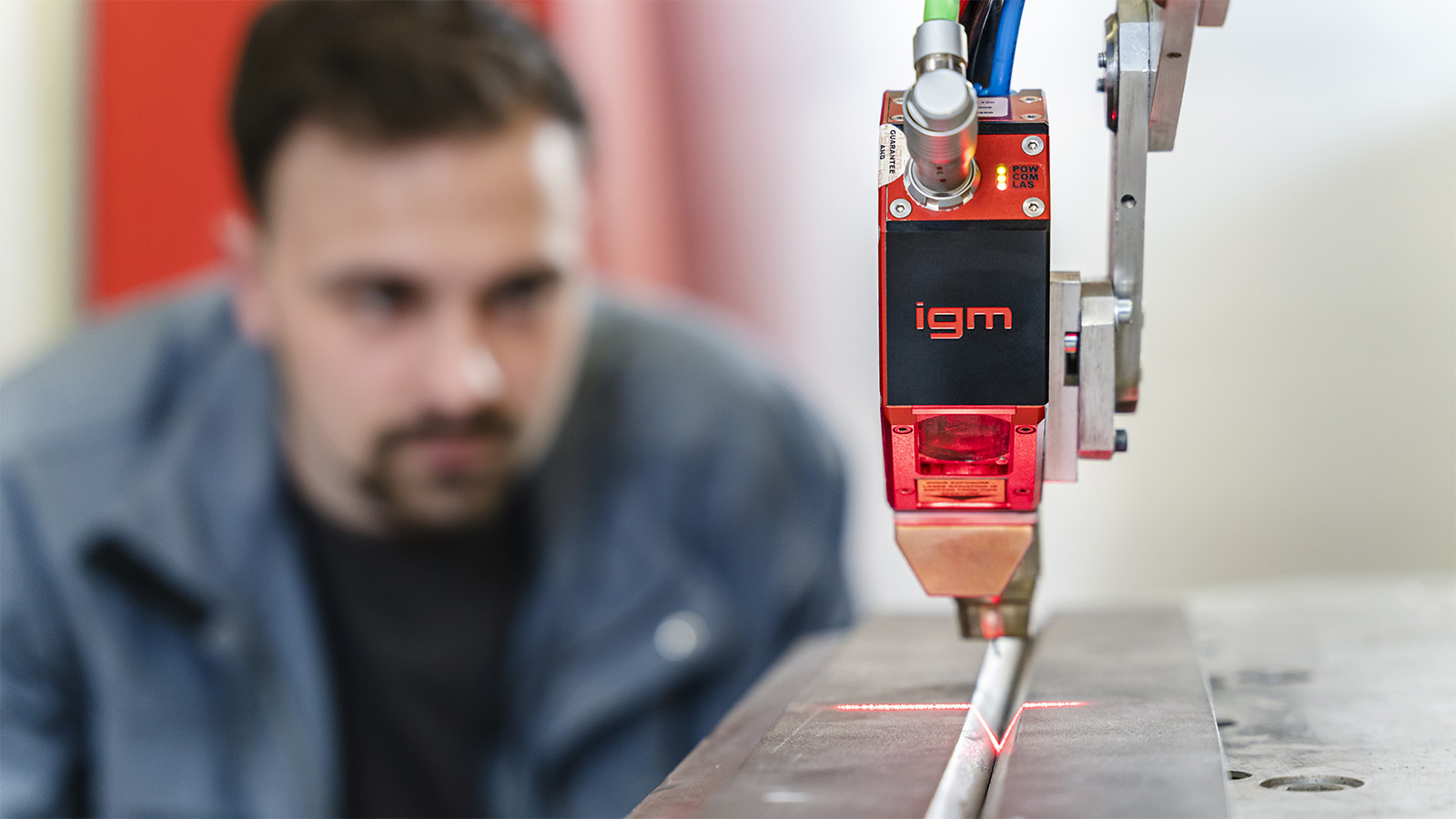
Gas nozzle search – tactile sensor for position detection
Tactile sensor used to determine the workpiece position or its components and individual parts by gauging the surface of the workpiece. In each case, the successional part of the program is shifted according to determined deviations.
Sensor shifting may be applied for correction of an arbitrary amount of individual points, sections of a welding program or entire programs. Combination with arc seam sensing is feasible. The control system supports shifting, rotating and tilting of a program, depending on position change.
Sensor types:
05. cont.
Arc seam sensing – precision welding of fillet and V-seams
During the welding process arc seam sensing is used to compensate for positional tolerances of the welding seam.
By means of a special software and specifically designed hardware, the actual seam position of fillets and V-shaped joints is computed by processing data measured, while arc weaving gives a corresponding shift of the original programmed point(s) to the true seam position. This arc seam sensing technique can be used with a complete range of welding transfers such as short arc, spray arc and pulsed arc welding – using single or Tandem applications. The welding torch then follows the path of the seam joint exactly.
This process can be advantageous in combination with gas nozzle sensing. There, the starting point of each welding seam is detected by the sensor and the arc is ignited at the correct position with the desired stick-out.
igm laser camera iCAM
In order to enable the robot to always find the right direction, extremely effective, compact laser cameras are used. They are designed for tracking different welding seam types, for identifying and measuring detected gaps, and for online compensation of volumes variations.
The camera design is based on synchronized laser scan technology, featuring high speed stability, large and programmable workspace, deep visual range, and robustness regarding ambient light and reflections. Impassivity against high frequencies and magnetic fields makes it an ideal device for many industrial processes under rough conditions.
The igm laser camera iCAM is mounted on the wrist axis of the robot. It measures the position and volume of the weld groove online and adjusts the robot movement and the welding parameters accordingly. For the application with welding in narrow workpiece ranges, the camera can be automatically deposited and readopted during the welding program. This laser camera iCAM, developed by igm, offers as an outstanding feature the complete integration into the robot control. Thus programming is done with the igm teach pendant K6 without the need for an additional PC. The user benefits from the wide range of languages, European as well as Asian ones, being supported by the robot software. By means of the logging function, the whole joint geometry can be displayed, indicating gaps and volumes. A live view of the measuring field is given by greyscale value image.
igm laser sensor iLS-C
The igm laser sensor iLS-C is useful for applications when edges or gaps must be searched for. The sensor is conceived to detect deviations between the actual workpiece position and its original position. Shifting is computed in parallel as well as in 3D mode, effectively compensating height and width deviations.
Compared with conventional tactile sensors, this laser sensor reduces non-productive times essentially by using high searching speeds and detecting height and lateral position during a single search path simultaneously. The well-designed teach pendant supports easy programming; special knowledge regarding processing algorithms is not required.
iLS-C shall typically be applied in those cases when tactile sensing is not possible due to sheet thicknesses and / or accessibility.
Detection is initiated by moving the sensor with the robot torch across the seam to be searched for. Always the entire search sequence is performed and then the image is analyzed. Thus interference such as peaks, freak values (mirror effects) or parasitic objects (spatter formation and debris) may be identified and filtered out. The seam type to be searched for must be assigned to the search sequence. The sensor computes the detected point’s absolute position according to certain robot parameters and transmits the data to the robot control system.

06.
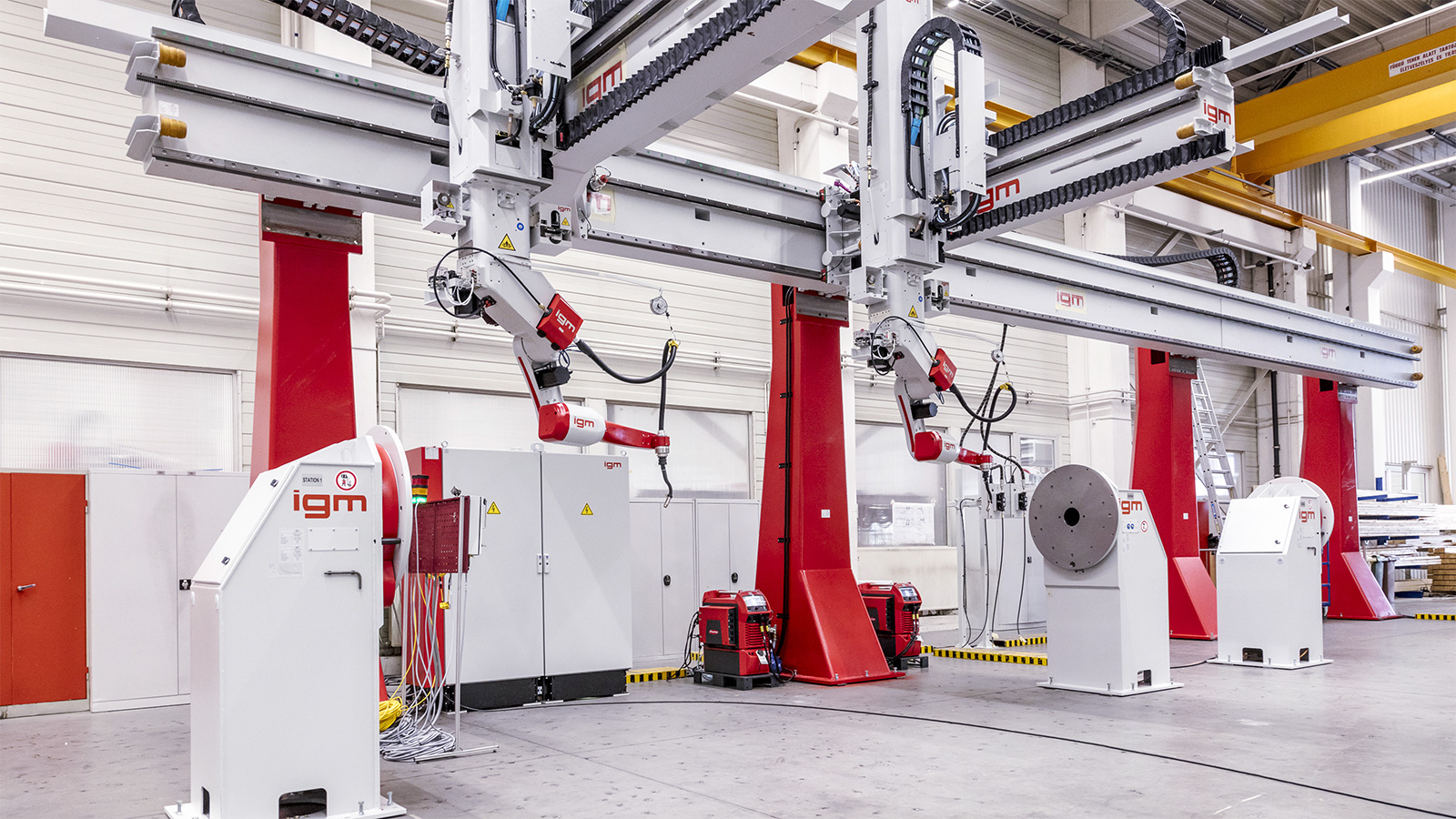
igm robot periphery
The robot is mounted on the robot periphery in an upright or suspended position. The external axes of the track systems are fully integrated in the control system as NC axes, significantly extending the working area of the robot.
A variety of different rotating and linear units are available, either as single axes or combined with up to 3 positioning units. It’s also possible that several robots share a track axis. The positioning range of a longitudinal axis is up to 100m+.
Periphery types:
06. cont.
igm robot periphery
The robot is mounted on the robot periphery in an upright or suspended position. The external axes of the track systems are fully integrated in the control system as NC axes, significantly extending the working area of the robot.
A variety of different rotating and linear units are available, either as single axes or combined with up to three positioning units. It is also possible that several robots share a track axis. The positioning range of a longitudinal axis is up to 100m and more.
igm workpiece periphery
The workpiece periphery holds, positions, and moves workpieces. The external axes are fully integrated in the control systems as NC axes and, in addition, feature manual control functionality. External axes may be included in workpiece manipulation during execution of welding steps. Using the teach pendant, they are programmed together with the robot axes.
A variety of different rotary modules is available, as a single axis or combined with up to three axes with a load capacity of up to 25,000kg and more.
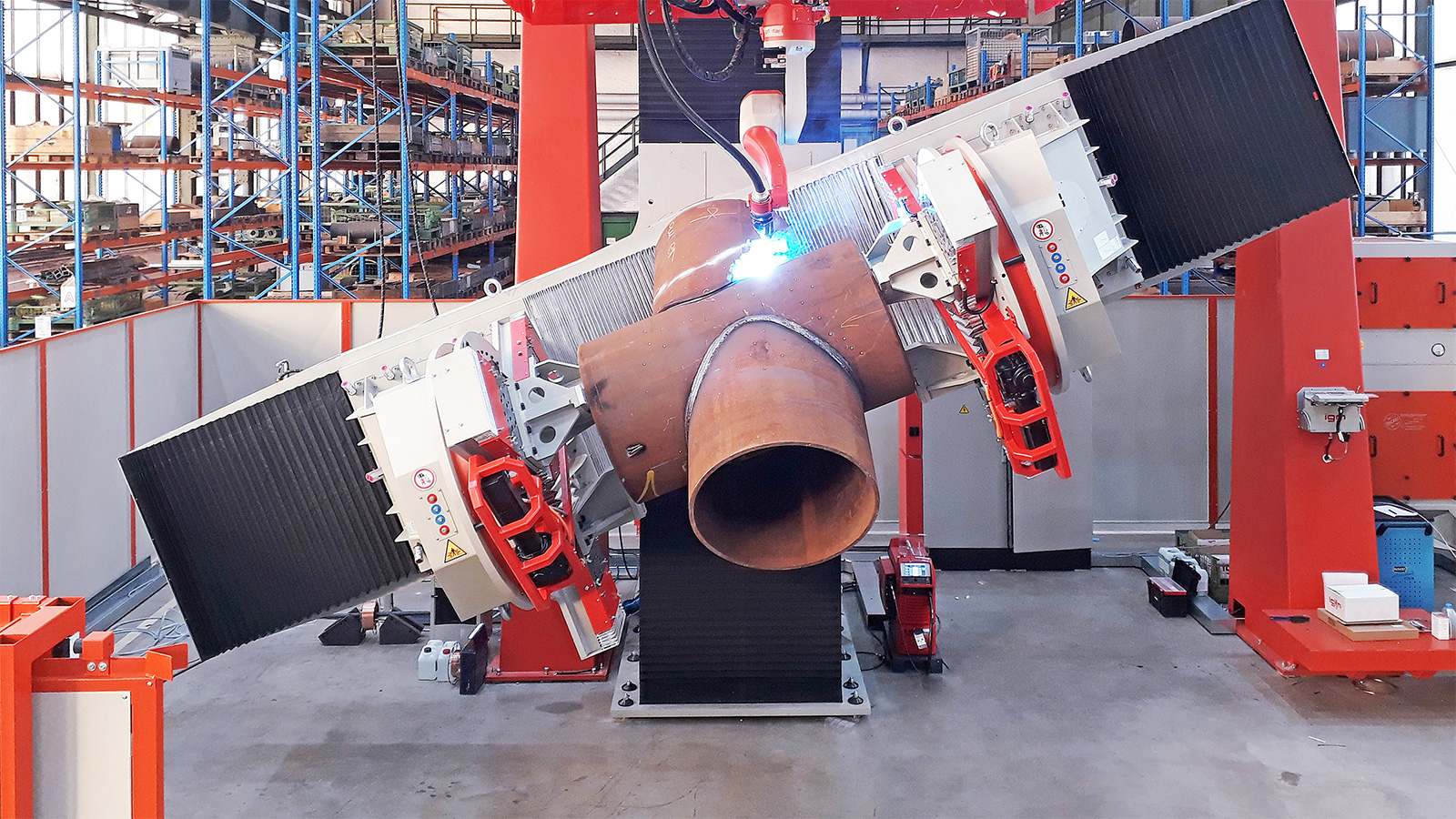
igm portal systems
igm offers portal gantry systems for welding large-scale components, customized for individual applications. Portal gantry systems range from a track gauge of 3 to 25m with vertical tracks of up to 6m stroke.
One or two robots may be mounted on a portal; since the portal axis is controlled by the robot control system, it may also be used for positioning during execution of a welding step.
The standard portal design includes a double-sided rack drive with AC servo motors, stable wheel house with integrated edge guide control on massive rails, moving control cabinet, power source, and a control desk, if requested.

07.
Optimised for arc welding
The igm compact systems are optimized for arc welding applications in all mechanical aspects, as well as the control hardware and software. In this combination of workpiece and robot peripherals, the entire system is kept compact, since the robot changes workstations simply by pivoting the rotary arm or, the workstation change is performed by a rotary table.
Examples of igm compact systems and complete welding cells:
07. cont.
Additional axes
The drive is axis-controlled and provided by an AC servo motor with a special gearbox and a built-in digital encoder. The turning fixture is perfect for use as an external robot axis.
Synchronised movement
Workpiece movement is completely integrated in the robot control system and permits synchronised movement of the workpiece during the welding sequence.
Programmed via K6
The programming takes place simply via the teach pendant K6. All necessary control components for manual and automatic operation are integrated in the system.

08.
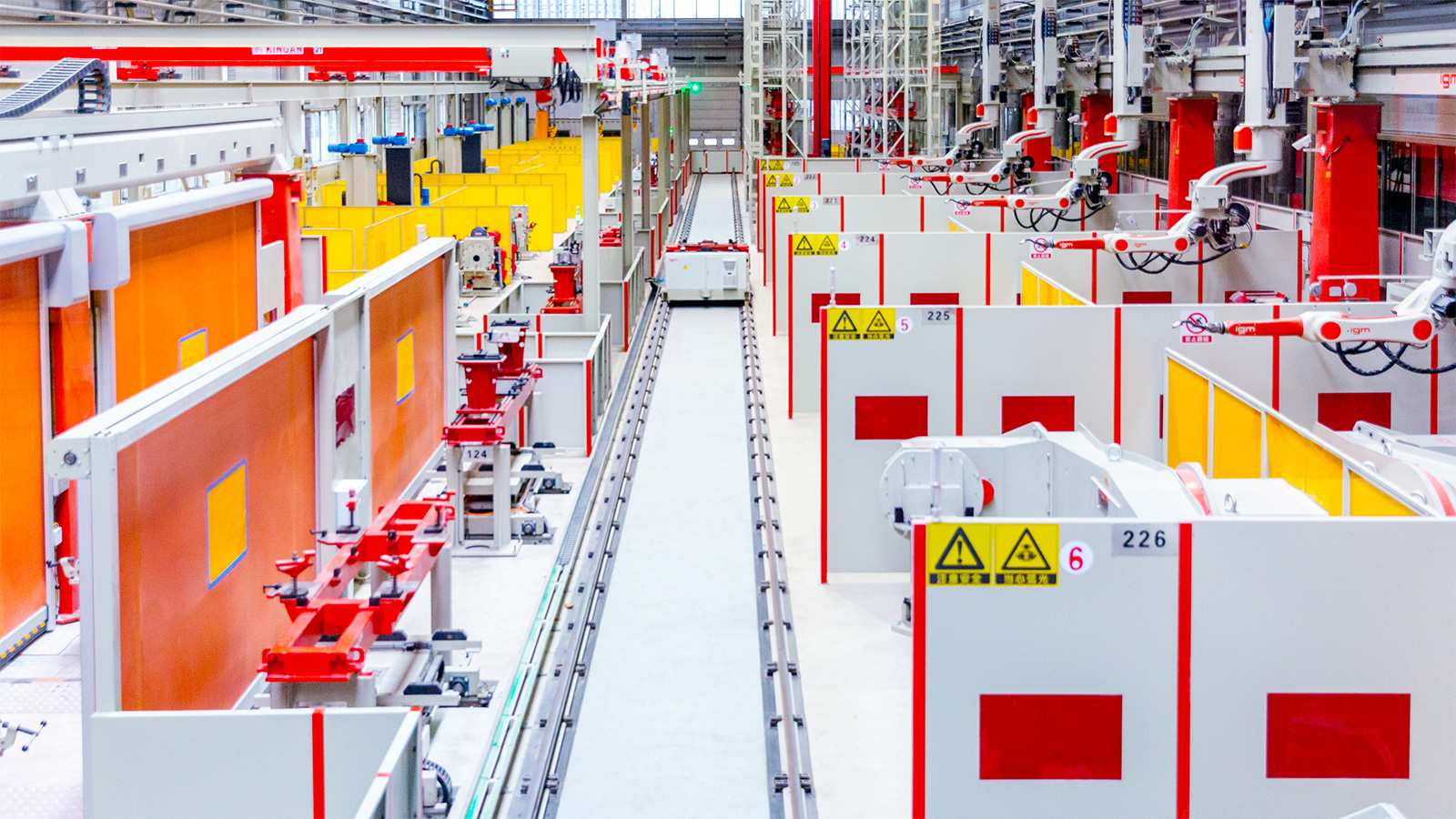
FMS – Flexible manufacturing system – customised by igm for your purpose
For special applications, igm produces customized welding systems fulfilling your individual requirements. The applications successfully installed range from gas bottles machines, flexible manufacturing cells to complete production lines.
Components of manufacturing lines:
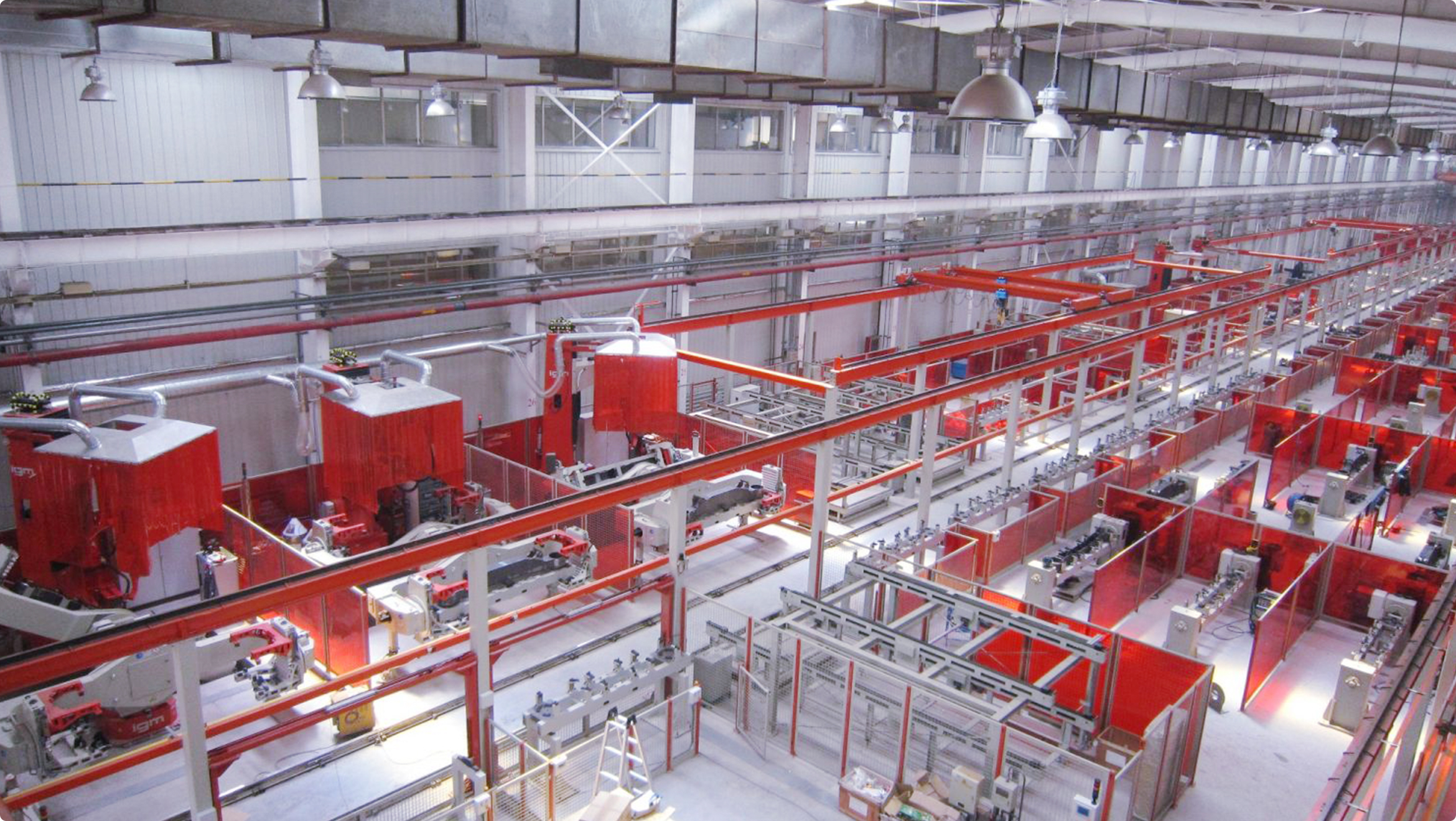

08. cont.
Customised robot systems
In these flexible systems more than just the welding technology is required: loading, conveying, stretching, bending, cutting, measuring, manipulating, editing, storing, unloading, controlling.
Complex manufacturing tasks require flexible solutions. igm has many years’ experience in engineering and realisation of full automatic manufacturing lines for various piece parts. For additional production requirements we provide handling devices, we develop special purpose machines and take care of your whole project as a main contractor, from order placing up to final commissioning.
Basic concepts of flexible manufacturing lines:
The whole fabrication line including the robot cells is controlled by one single host computer. Graphic information on the display makes operation and monitoring easy.
Workpieces of totally different shapes and dimensions are handled by specially designed pallets. The inner side of these pallets is designed to clamp the piece parts while the vertical outer side represents the patente clamping device on the positioner’s face plate. A built-in sensor monitors the correct clamping.
The conveyor carriage with a satellite carriage and a scissor-table conveys the parts to the robot station, where they are clamped automatically. In each feeding-station the main conveyor is pneumatically indexed with the aim to assure a correct position in relation to the rails of the satellite carriage.

09.
Performance under harsh conditions
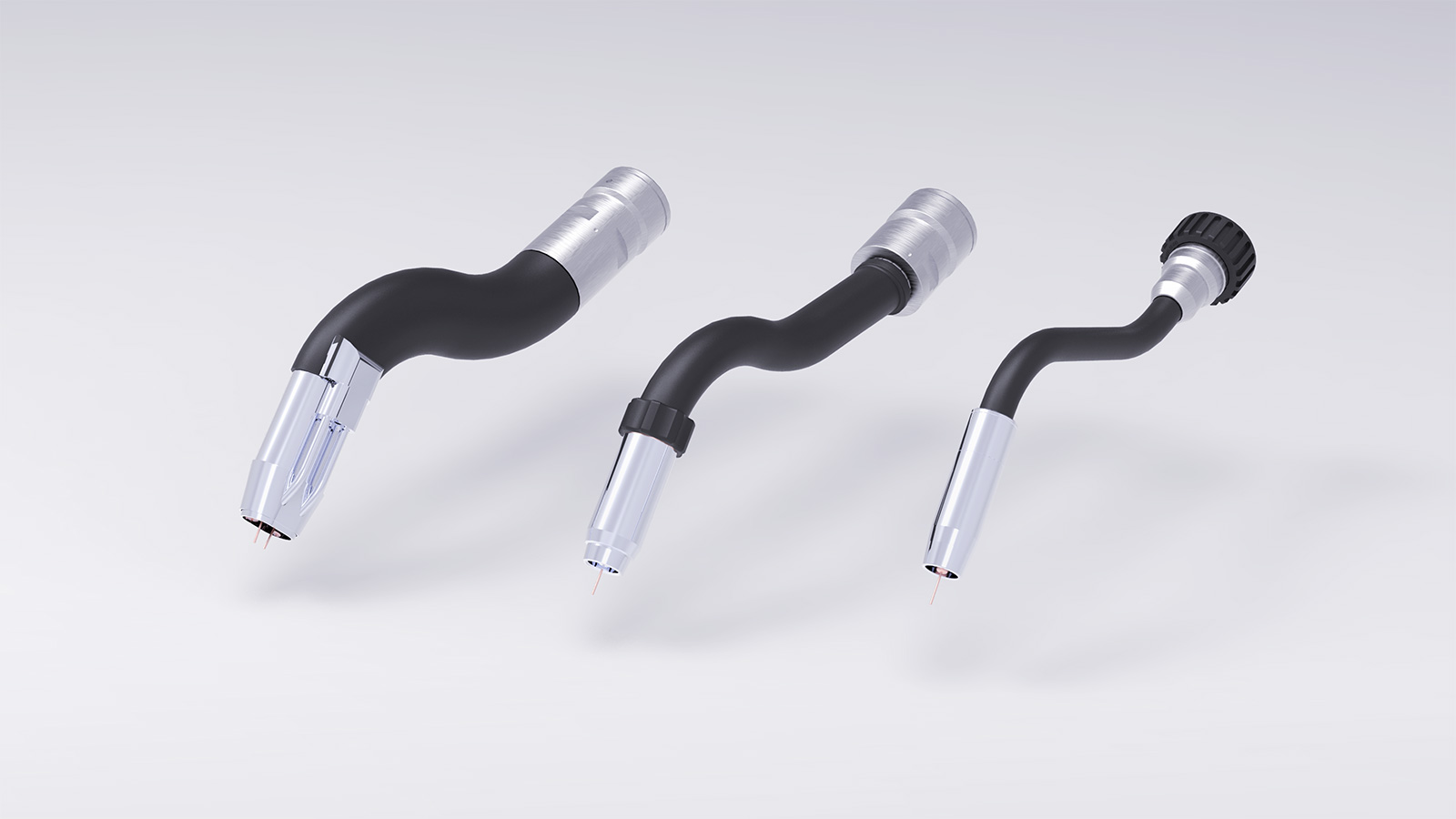
The welding torches are designed for use on robots for high-performance welding under harsh conditions. The slim design, together with the swan’s neck shape, permits the best accessibility even in narrow parts of the work piece. All welding torches provided as standard for igm robots have a particularly stable design with intensive water cooling and a quick-release coupling. They are also configured for pneumatic torch cleaning with compressed air at least 7 bar and for the use of the gas nozzle as a tactile sensor for program shifts.
Typical benefits:
09. cont.
igm torch exchange system
By means of this torch exchange system the robot can automatically be equipped with torches of various geometries. This functionality is program-controlled and can be applied wherever appropriate and needed. The torches to be used can be of different length or special shape, designed for better accessibility to narrow areas.
In any case the welding media are lead through the hollow shaft in the robot’s wrist joint offering the large working envelope and the outstanding performance of the robot when welding in narrow spaces of the work piece. The exchange system is designed in such a way, that the torch will be decoupled from the hose package.
The exchange system is designed to seperate the welding torch completely from all media of the hose package. The torch magazine is mounted stationary on a stand or on a pillar. A variety of torches can be exchanged, whereby also switching between tandem and single-wire process is possible.
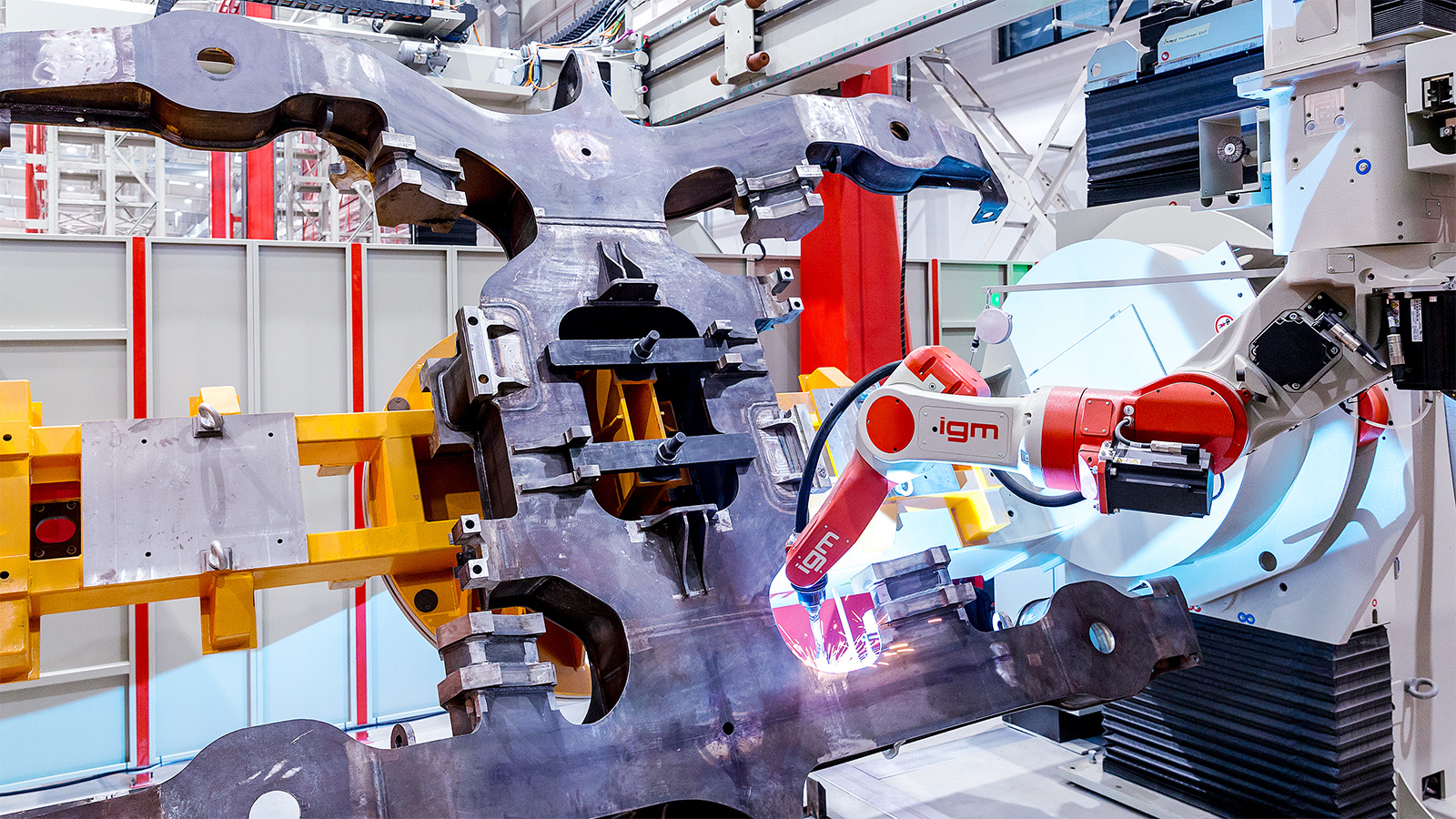
10.
Welding and cutting processes
igm robots may be used for all non-contact welding and cutting processes. Power sources from many well-known manufacturers can be integrated with our robot systems for welding and cutting applications. Products range from digital inverter power sources for MIG/MAG welding, TIG applications, plasma cutting and welding apparatus to high-capacity devices for the tandem process.
Depending on material and sheet thickness, following processes are used:
10. cont.
Brushing, Grinding and Handling - Manipulation using Robots
Through the possibilities afforded by a modular configuration of robot cells and the integration of diverse tools in the robot control sequence, significantly better throughput times and constant process qualities can be achieved.
We will be pleased to utilise our 40 years of experience in the sphere of realising complete customised solutions with the aid of a robot, not only in the welding sector. Innumerable examples of applications in other sectors speak for themselves.
As a specialist of customised solutions, igm undertakes the complete designing of the necessary machines.

11.
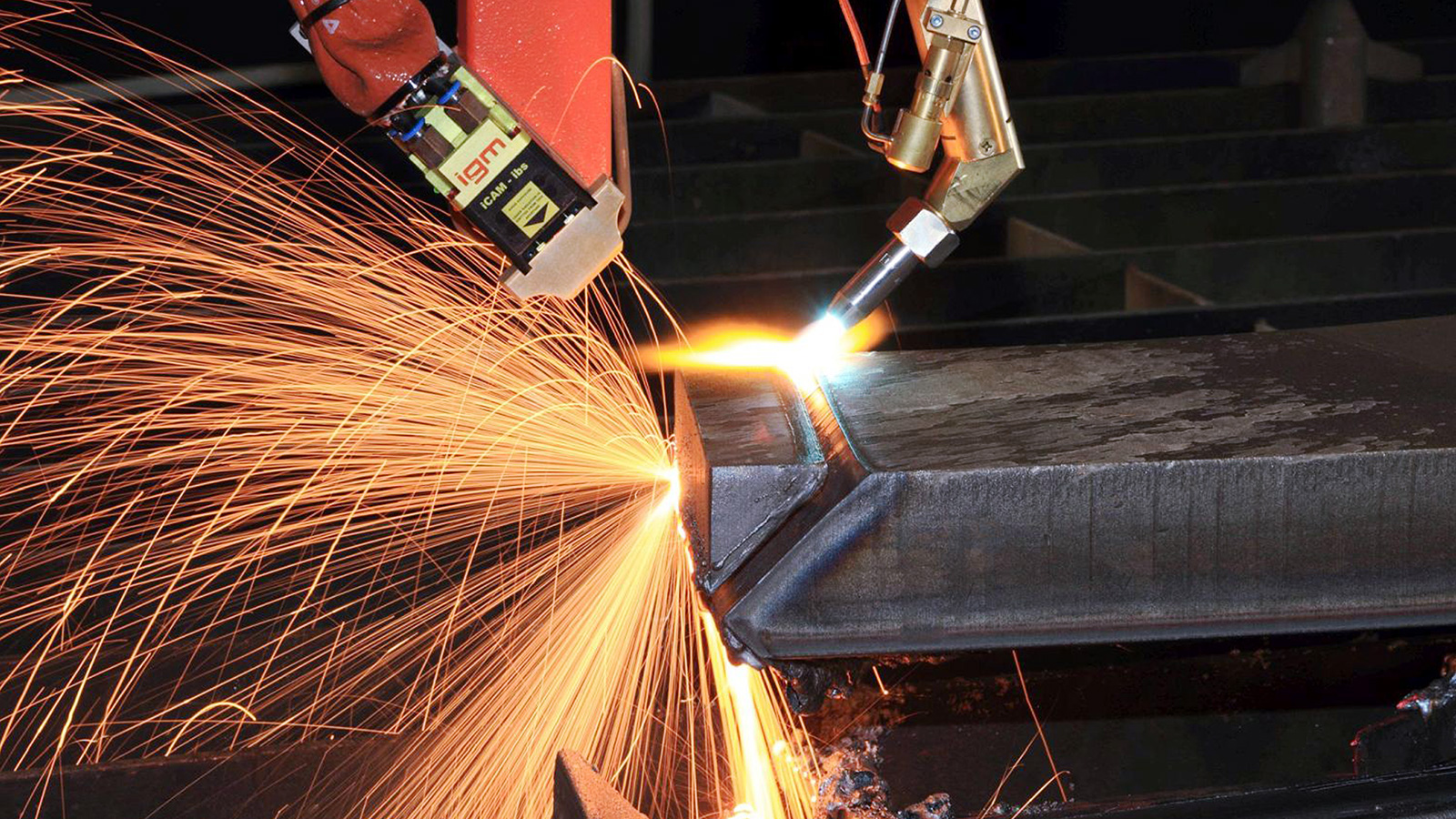
Automatic welding seam preparation
Sensor-controlled bevelling system for automated welding seam preparation of flat steel plates. The stable portal construction including application-oriented design of the cutting head supports all types of upper side or bottom side cuts with sensor-controlled online edge tracking.
Automatic sheet thickness measurement:
A highly accurate seam joint preparation while maintaining a specified land height or a specified seam volume requires not only the exact tracking of the cutting torch along the contour but also the exact detection of the sheet thickness. For this purpose, the igm bevelling machine can be equipped with an automatic sheet thickness measurement.
11. cont.
Tolerance of +/- 0.5mm
A laser camera measures the workpiece position and tracks along the upper edge, ensuring the requested land heights with a tolerance of +/- 0.5mm even compensating heat distortion. The system processes the required bevels, which are defined by simply clicking and inserting the geometry parameters in a CAD drawing of the component, with the specially developed software.
Sensor supported systems can be provided with the igm iBS oxy and plasma cutting machine which are optimised for all mechanical and control requirements for chamfering flat sheet metal. This special characteristic was made possible by the development of a parallelogram-like cutting head, on which the cutting torch, movable in two axes, is mounted.
This unit is fitted onto a stable gantry, running on rails, with a cross slide and a vertical slide to take up the parallelogram. The special design of the cutting head allows chamfering of flat sheet metal with any and also alterable chamfer angles on straight or curved cuts.